Toenail fungal infection or onychomycosis is an infectious disease and is a fairly common pathology.The prevalence of toenail injuries in all countries of the world ranges between 18 and 45%.Onychomycosis often occurs in elderly people, cancer patients, and patients with diabetes mellitus, Kaposi's sarcoma, and ichthyosis.
Onychomycosis is not just a cosmetic problem.It represents a serious threat to the human body, since the products of the vital activity of the fungus (xanthomegin, viomellin, antibiotic-like substances and penicillin) cause prolonged persistence in the affected nails and can lead to the development of liver disease, drug-induced toxicoderma and even Lyell's syndrome.
Etiology and epidemiology.
The causative agents of onychomycosis are represented by three groups of fungi:
- dermatophytes (up to 95%) - Trichophyton rubrum (causes damage to the nails of the feet and hands, as well as the skin), Trichophytonmentagrophytes (affects the nails of the first and fifth fingers and the skin of 3-4 interdigital folds), Epidermophytonfloccosum (nails of the first and fifth fingers);
- Yeast fungi (up to 4%) - Candida spp.(first affects the skin around the nails, and then penetrates the nail plate);
- molds (up to 1%): Fusarium and Alternaria (most frequently found in immunodeficiency states).
Isolated onychomycosis is rare;Most often, simultaneous lesions are observed on the skin of the feet, scalp and smooth skin.
Infection occurs through household items: bath mat, slippers, towel, manicure accessories;as well as when visiting a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool.Men are more susceptible to this pathology than women.Most adults suffer from onychomycosis;Among children, cases of nail mycosis are rare.
The risk group includes bath attendants, military personnel, athletes, people who regularly visit baths and saunas, and miners.
The source of infection is the skin on the feet of an infected person;sometimes entire families are affected.
pathogeny
Onychomycosis is a source of fungal infection that can cause sensitization of the body.In addition, mushrooms release substances toxic to the human body.
Predisposing factors for infection are lesions on the skin of the feet and nails that occur when tight shoes squeeze the toes;humid and hot environment created by some low-quality shoes made of unnatural materials;the presence of serious diseases, immunodeficiency states, old age.
Symptoms of the disease
According to the differences in symptoms, four forms of onychomycosis are distinguished:
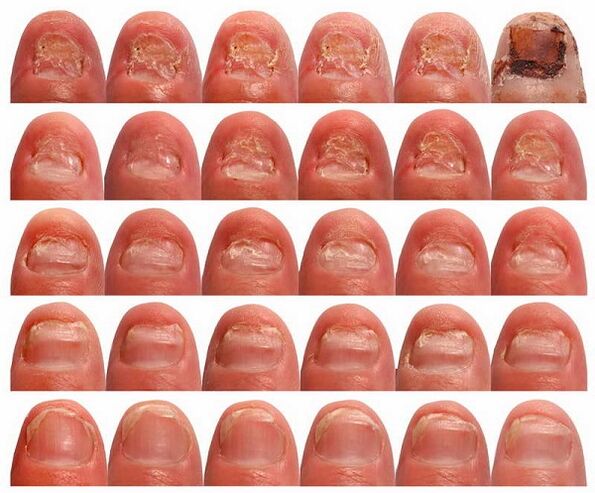
- Distal lateral (subungual) onychomycosisthe most common.The causative agents are trichophyton red, candida and, very rarely, mold.In this type of lesion, the nail bed fungus enters from the skin through the free edge of the nail and spreads towards the matrix.In this case, the nail plate, due to hyperkeratosis, gradually moves away from the bed and acquires a yellowish color.Thickening of the nail plate may occur, and bacterial contamination gives the nail a variety of colors ranging from greenish to dirty brown.
- White superficial onychomycosismost commonly caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, which causes white spots to form on the surface of the nail plate;As the process progresses, these points merge.This type of onychomycosis occurs in elderly patients with toe deformity, in which one toe covers the adjacent one.The nail plate becomes dystrophic, crumbles and acquires a grayish or brownish color, but the matrix and epithelium of the bed are not affected and inflammatory phenomena do not occur on the skin.
- Proximal subungual onychomycosisthe rarest type in which the pathogen, most often trichophyton red, penetrates the nail plate from the skin or from the periungual fold, then spreads along it and reaches the matrix and distal parts of the nail plate.As a result, extensive detachment of the nail plate is observed.With secondary bacterial contamination, the nail plate changes color.
- Total dystrophic onychomycosisIt develops as a complication of the distal lateral or, much less frequently, proximal subungual, and also occurs in chronic subcutaneous candidiasis.With this form the entire nail is affected with its complete destruction;the nail fold is absent or pathologically thickened, while a normal nail plate cannot form.
All onychomycosis must be differentiated from psoriasis, eczema, lichen planus and other skin diseases.To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform microscopy of the pathological material of the lesion and culture of the pathogen on special identification media.
Onychomycosis treatment
When prescribing treatment to a patient with onychomycosis, a number of factors must be taken into account: the type of pathogen, the prevalence of the process, the general condition of the patient and his financial capabilities.
- Local agents are often used in the treatment of distal and lateral subungual onychomycosis when no more than 3 nails are affected, as well as in patients for whom antifungal tablets are contraindicated.The most effective topical preparations include creams and varnishes.They are often combined to achieve a faster therapeutic effect.The preparations contain high concentrations of active ingredients;They act effectively on the surface of the nail plate, but cannot always penetrate to the nail bed, where the most persistent fungi are found.In such cases, the affected nail plate is removed surgically or with the help of special chemicals (keratolytics) and local treatment is continued.This method is inconvenient only because of the duration of the process, since it requires careful adherence to the treatment regimen throughout the entire time during which a healthy nail plate grows.In this case, ointments should be applied daily, and varnishes only once a week.
- Systemic therapy is more effective and reliable in the treatment of onychomycosis;It is used when local treatment fails.Indications for prescribing systemic drugs are the late stages of lateral and proximal distal subungual onychomycosis, as well as total onychomycosis.
The choice of drug for systemic treatment must be justified taking into account the pharmacokinetics, spectrum of action and antifungal activity of each drug.We must not forget that any drug can provide a pronounced therapeutic effect if prescribed properly.